
|
|
PDF LPV324MX Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | LPV324MX | |
| Descripción | General Purpose / Low Voltage / Low Power / Rail-to-Rail Output Operational Amplifiers | |
| Fabricantes | National Semiconductor | |
| Logotipo | ||
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de LPV324MX (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 21 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
August 1999
LPV321 Single/ LPV358 Dual/ LPV324 Quad
General Purpose, Low Voltage, Low Power, Rail-to-Rail
Output Operational Amplifiers
General Description
The LPV321/358/324 are low power (9µA per channel at
5.0V) versions of the LMV321/358/324 op amps. This is an-
other addition to the LMV321/358/324 family of commodity
op amps.
The LPV321/358/324 are the most cost effective solutions
for the applications where low voltage, low power operation,
space saving and low price are needed. The
LPV321/358/324 have rail-to-rail output swing capability and
the input common-mode voltage range includes ground.
They all exhibit excellent speed-power ratio, achieving
152 KHz of bandwidth with a supply current of only 9µA.
The LPV321 is available in space saving SC70-5, which is
approximately half the size of SOT23-5. The small package
saves space on pc boards, and enables the design of small
portable electronic devices. It also allows the designer to
place the device closer to the signal source to reduce noise
pickup and increase signal integrity.
The chips are built with National’s advanced submicron
silicon-gate BiCMOS process. The LPV321/358/324 have bi-
polar input and output stages for improved noise perfor-
mance and higher output current drive.
Features
(For V+ = 5V and V− = 0V, Typical Unless Otherwise Noted)
jGuaranteed 2.7V and 5V Performance
jNo Crossover Distortion
jSpace Saving Package
SC70-5
2.0x2.1x1.0mm
jIndustrial Temp.Range
−40˚C to +85˚C
jGain-Bandwidth Product
152KHz
jLow Supply Current
LPV321
9µA
LPV358
15µA
LPV324
28µA
jRail-to-Rail Output Swing
@ 100kΩ Load
V+−3.5mV
V−+90mV
jVCM
−0.2V to V+ −0.8V
Applications
n Active Filters
n General Purpose Low Voltage Applications
n General Purpose Portable Devices
Connection Diagrams
5-Pin
SC70-5/SOT23-5
14-Pin SO/TSSOP
DS100920-1
Top View
8-Pin SO/MSOP
DS100920-3
Top View
DS100920-2
Top View
© 1999 National Semiconductor Corporation DS100920
www.national.com
1 page 
5V AC Electrical Characteristics
Unless otherwise specified, all limits guaranteed for T J = 25˚C, V+ = 5V, V− = 0V, VCM = 2.0V, VO = V+/2 and R L > 1 MΩ.
Boldface limits apply at the temperature extremes.
Symbol
Parameter
Conditions
Typ
(Note 6)
Limit
(Note 7)
Units
SR Slew Rate
(Note 9)
0.1
V/µs
GBWP
Φm
Gm
en
Gain-Bandwidth Product
Phase Margin
Gain Margin
Input-Referred Voltage Noise
CL = 22 pF
f = 1 kHz,
152
87
19
146
KHz
Deg
dB
in Input-Referred Current Noise f = 1 kHz
0.30
Note 1: Absolute Maximum Ratings indicate limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. Operating Ratings indicate conditions for which the device is in-
tended to be functional, but specific performance is not guaranteed. For guaranteed specifications and the test conditions, see the Electrical Characteristics.
Note 2: Human body model, 1.5 kΩ in series with 100 pF. Machine model, 0Ω in series with 200 pF.
Note 3: Shorting output to V+ will adversely affect reliability.
Note 4: Shorting output to V- will adversely affect reliability.
Note 5: The maximum power dissipation is a function of TJ(max), θJA, and TA. The maximum allowable power dissipation at any ambient temperature is
P D = (TJ(max)–TA)/θJA. All numbers apply for packages soldered directly into a PC board.
Note 6: Typical values represent the most likely parametric norm.
Note 7: All limits are guaranteed by testing or statistical analysis.
Note 8: RL is connected to V -. The output voltage is 0.5V ≤ VO ≤ 4.5V.
Note 9: Connected as voltage follower with 3V step input. Number specified is the slower of the positive and negative slew rates.
Note 10: All numbers are typical, and apply for packages soldered directly onto a PC board in still air.
5 www.national.com
5 Page 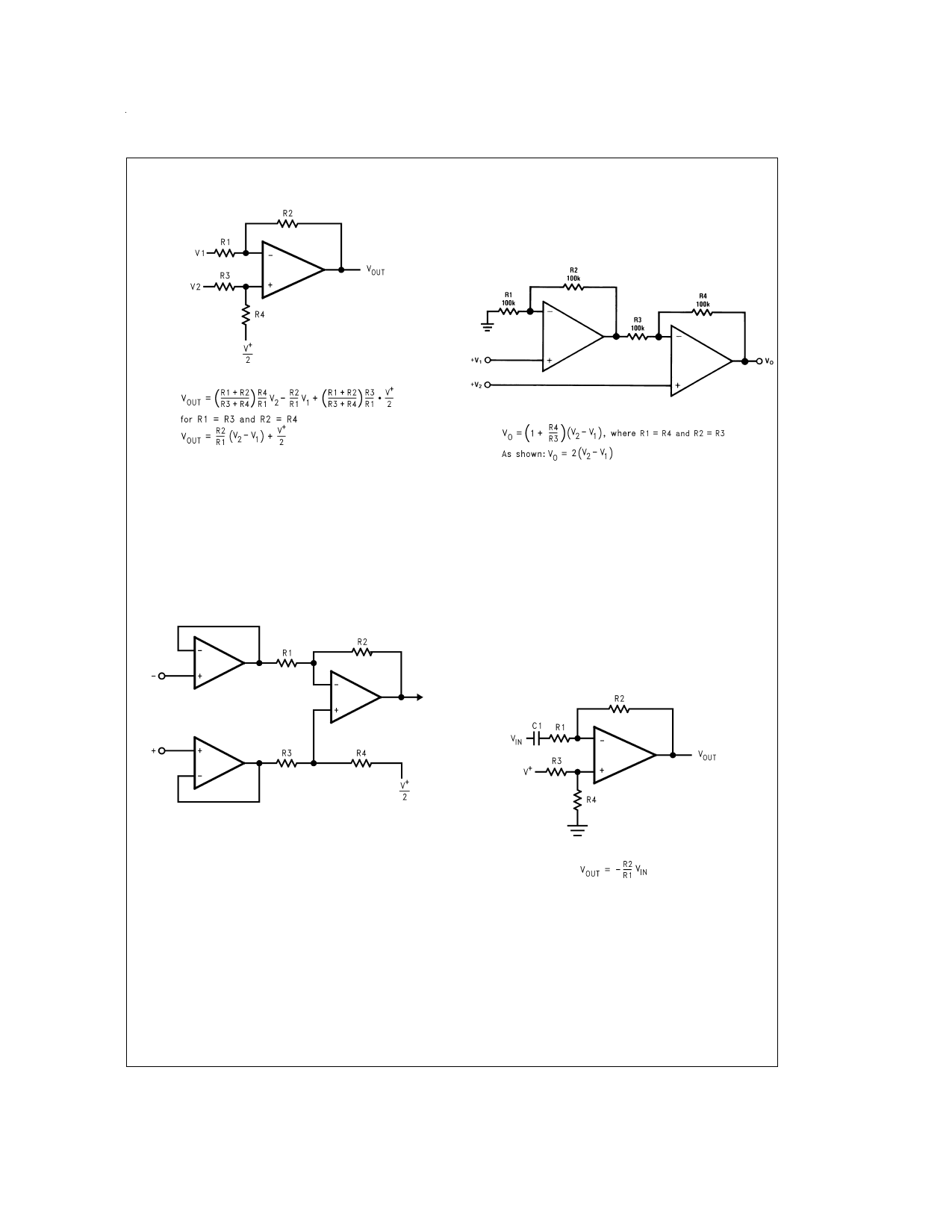
Application Notes (Continued)
4.2.2 Two-op-amp Instrumentation Amplifier
A two-op-amp instrumentation amplifier can also be used to
make a high-input-impedance DC differential amplifier (Fig-
ure 7). As in the three-op-amp circuit, this instrumentation
amplifier requires precise resistor matching for good CMRR.
R4 should equal to R1 and R3 should equal R2.
DS100920-7
DS100920-11
FIGURE 5. Difference Amplifier
4.2 Instrumentation Circuits
The input impedance of the previous difference amplifier is
set by the resistor R1, R2, R3, and R 4. To eliminate the prob-
lems of low input impedance, one way is to use a voltage fol-
lower ahead of each input as shown in the following two in-
strumentation amplifiers.
4.2.1Three-op-amp Instrumentation Amplifier
The quad LPV324 can be used to build a three-op-amp in-
strumentation amplifier as shown in Figure 6
FIGURE 7. Two-op-amp Instrumentation Amplifier
4.3 Single-Supply Inverting Amplifier
There may be cases where the input signal going into the
amplifier is negative. Because the amplifier is operating in
single supply voltage, a voltage divider using R3 and R4 is
implemented to bias the amplifier so the input signal is within
the input common-common voltage range of the amplifier.
The capacitor C1 is placed between the inverting input and
resistor R1 to block the DC signal going into the AC signal
source, VIN. The values of R1 and C1 affect the cutoff fre-
quency, fc = 1/2π R 1C1.
As a result, the ouptut signal is centered around mid-supply
(if the voltage divider provides V+/2 at the non-inverting in-
put). The output can swing to both rails, maximizing the
signal-to-noise ratio in a low voltage system.
DS100920-85
FIGURE 6. Three-op-amp Instrumentation Amplifier
The first stage of this instrumentation amplifier is a
differential-input, differential-output amplifier, with two volt-
age followers. These two voltage followers assure that the
input impedance is over 100MΩ. The gain of this instrumen-
tation amplifier is set by the ratio of R2/R 1. R3 should equal
R1 and R4 equal R2. Matching of R3 to R1 and R4 to R2 af-
fects the CMRR. For good CMRR over temperature, low drift
resistors should be used. Making R4 Slightly smaller than R
2 and adding a trim pot equal to twice the difference between
R 2 and R4 will allow the CMRR to be adjusted for optimum.
DS100920-13
FIGURE 8. Single-Supply Inverting Amplifier
4.4 Active Filter
4.4.1 Simple Low-Pass Active Filter
The simple low-pass filter is shown in Figure 9. Its
low-frequency gain(ω → o) is defined by −R3/R1. This allows
low-frequency gains other than unity to be obtained. The fil-
ter has a −20dB/decade roll-off after its corner frequency fc.
R2 should be chosen equal to the parallel combination of R1
and R3 to minimize errors due to bais current. The frequency
response of the filter is shown in Figure 10
11 www.national.com
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 21 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet LPV324MX.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| LPV324M | General Purpose / Low Voltage / Low Power / Rail-to-Rail Output Operational Amplifiers | National Semiconductor |
| LPV324MT | General Purpose / Low Voltage / Low Power / Rail-to-Rail Output Operational Amplifiers | National Semiconductor |
| LPV324MTX | General Purpose / Low Voltage / Low Power / Rail-to-Rail Output Operational Amplifiers | National Semiconductor |
| LPV324MX | General Purpose / Low Voltage / Low Power / Rail-to-Rail Output Operational Amplifiers | National Semiconductor |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
