
|
|
PDF P-80C32 Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | P-80C32 | |
| Descripción | P80C32 | |
| Fabricantes | ETC | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de P-80C32 (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 20 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
www.DataSheet4U.com
80C32/80C52
CMOS 0 to 44 MHz Single Chip 8–bit Microntroller
Description
TEMIC’s 80C52 and 80C32 are high performance CMOS
versions of the 8052/8032 NMOS single chip 8 bit µC.
The fully static design of the TEMIC 80C52/80C32
allows to reduce system power consumption by bringing
the clock frequency down to any value, even DC, without
loss of data.
The 80C52 retains all the features of the 8052 : 8 K bytes
of ROM ; 256 bytes of RAM ; 32 I/O lines ; three 16 bit
timers ; a 6-source, 2-level interrupt structure ; a full
duplex serial port ; and on-chip oscillator and clock
circuits. In addition, the 80C52 has 2 software-selectable
modes of reduced activity for further reduction in power
consumption. In the idle mode the CPU is frozen while
the RAM, the timers, the serial port and the interrupt
system continue to function. In the power down mode the
RAM is saved and all other functions are inoperative.
The 80C32 is identical to the 80C52 except that it has no
on-chip ROM. TEMIC’s 80C52/80C32 are manufactured
using SCMOS process which allows them to run from 0
up to 44 MHz with Vcc = 5 V.
TEMIC’s 80C52 and 80C32 are also available at 16 MHz
with 2.7 V < VCC < 5.5 V.
D 80C32 : Romless version of the 80C52
D 80C32/80C52-L16 : Low power version
Vcc : 2.7 – 5.5 V Freq : 0-16 MHz
D 80C32/80C52-12 : 0 to 12 MHz
D 80C32/80C52-16 : 0 to 16 MHz
D 80C32/80C52-20 : 0 to 20 MHz
D 80C32/80C52-25 : 0 to 25 MHz
D 80C32/80C52-30 : 0 to 30 MHz
D 80C32/80C52-36 : 0 to 36 MHz
D 80C32-40 : 0 to 40 MHz*
D 80C32-42 : 0 to 42 MHz*
D 80C32-44 : 0 to 44 MHz*
* 0 to 70°C temperature range.
For other speed and temperature range availability please consult your
sales office.
Features
D Power control modes
D 256 bytes of RAM
D 8 Kbytes of ROM (80C52)
D 32 programmable I/O lines
D Three 16 bit timer/counters
D 64 K program memory space
D 64 K data memory space
D Fully static design
D 0.8µ CMOS process
D Boolean processor
D 6 interrupt sources
D Programmable serial port
D Temperature range : commercial, industrial, automotive,
military
Optional
D Secret ROM : Encryption
D Secret TAG : Identification number
MATRA MHS
Rev. G (14 Jan. 97)
1
1 page 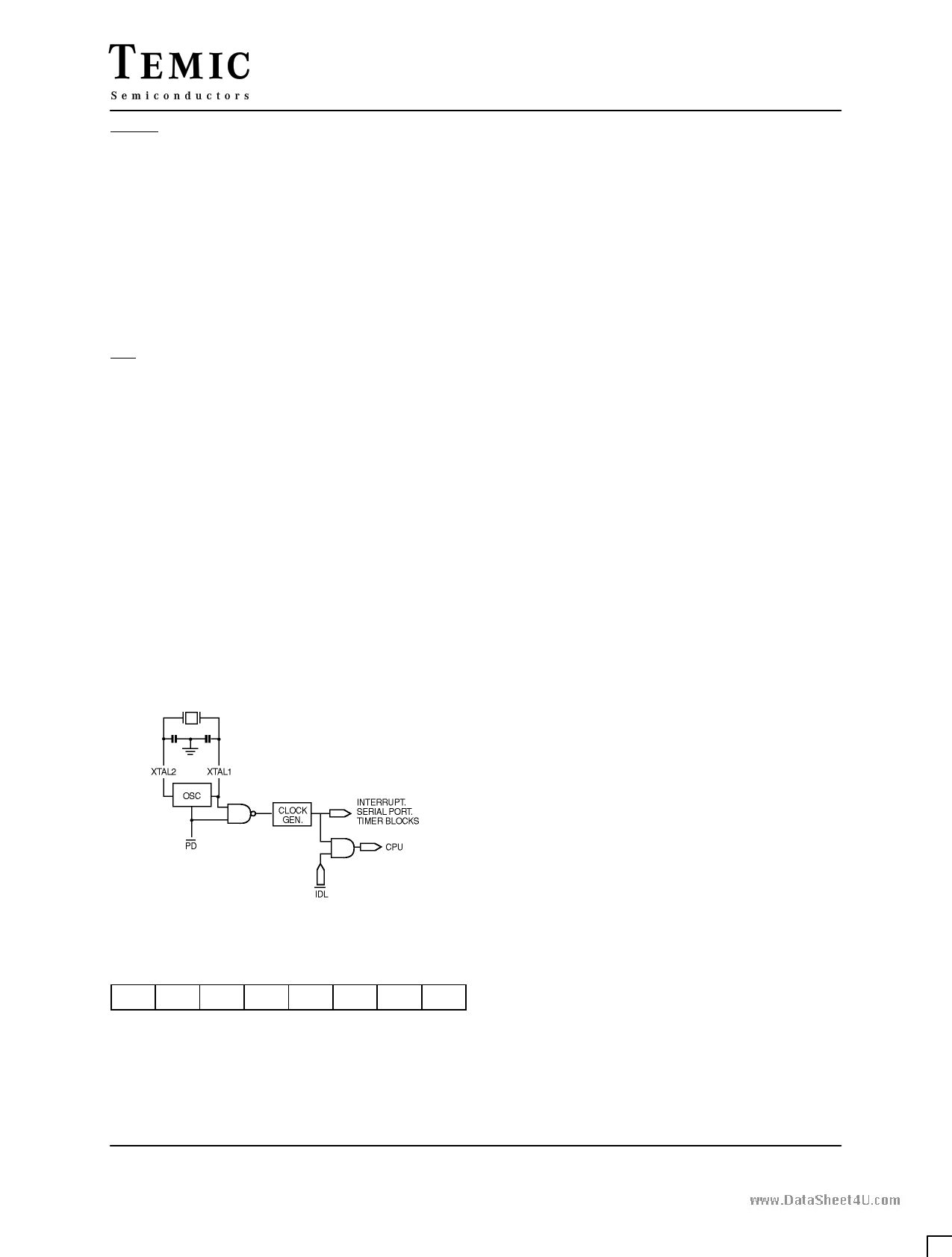
www.DataSheet4U.com
80C32/80C52
PSEN
Program Store Enable output is the read strobe to external
Program Memory. PSEN is activated twice each machine
cycle during fetches from external Program Memory.
(However, when executing out of external Program
Memory, two activations of PSEN are skipped during
each access to external Data Memory). PSEN is not
activated during fetches from internal Program Memory.
PSEN can sink/source 8 LS TTL inputs. It can drive
CMOS inputs without an external pullup.
1 FFFH). When EA is held low, the CPU executes only out
of external Program Memory. EA must not be floated.
XTAL1
Input to the inverting amplifier that forms the oscillator.
Receives the external oscillator signal when an external
oscillator is used.
XTAL2
EA
When EA is held high, the CPU executes out of internal
Program Memory (unless the Program Counter exceeds
Output of the inverting amplifier that forms the oscillator.
This pin should be floated when an external oscillator is
used.
Idle And Power Down Operation
Figure 3 shows the internal Idle and Power Down clock
configuration. As illustrated, Power Down operation
stops the oscillator. Idle mode operation allows the
interrupt, serial port, and timer blocks to continue to
function, while the clock to the CPU is gated off.
These special modes are activated by software via the
Special Function Register, PCON. Its hardware address is
87H. PCON is not bit addressable.
Figure 3.Idle and Power Down Hardware.
Symbol
Position
Name and Function
SMOD
–
–
–
GF1
GF0
PD
IDL
PCON.7
PCON.6
PCON.5
PCON.4
PCON.3
PCON.2
PCON.1
PCON.0
Double Baud rate bit. When set to
a 1, the baud rate is doubled when
the serial port is being used in
either modes 1, 2 or 3.
(Reserved)
(Reserved)
(Reserved)
General-purpose flag bit.
General-purpose flag bit.
Power Down bit. Setting this bit
activates power down operation.
Idle mode bit. Setting this bit
activates idle mode operation.
If 1’s are written to PD and IDL at the same time. PD
takes, precedence. The reset value of PCON is
(000X0000).
Idle Mode
PCON : Power Control Register
(MSB)
(LSB)
The instruction that sets PCON.0 is the last instruction
executed before the Idle mode is activated. Once in the
Idle mode the CPU status is preserved in its entirety : the
Stack Pointer, Program Counter, Program Status Word,
Accumulator, RAM and all other registers maintain their
data during idle. Table 1 describes the status of the
external pins during Idle mode.
SMOD – – – GF1 GF0 PD IDL
MATRA MHS
Rev. G (14 Jan. 97)
5
5 Page 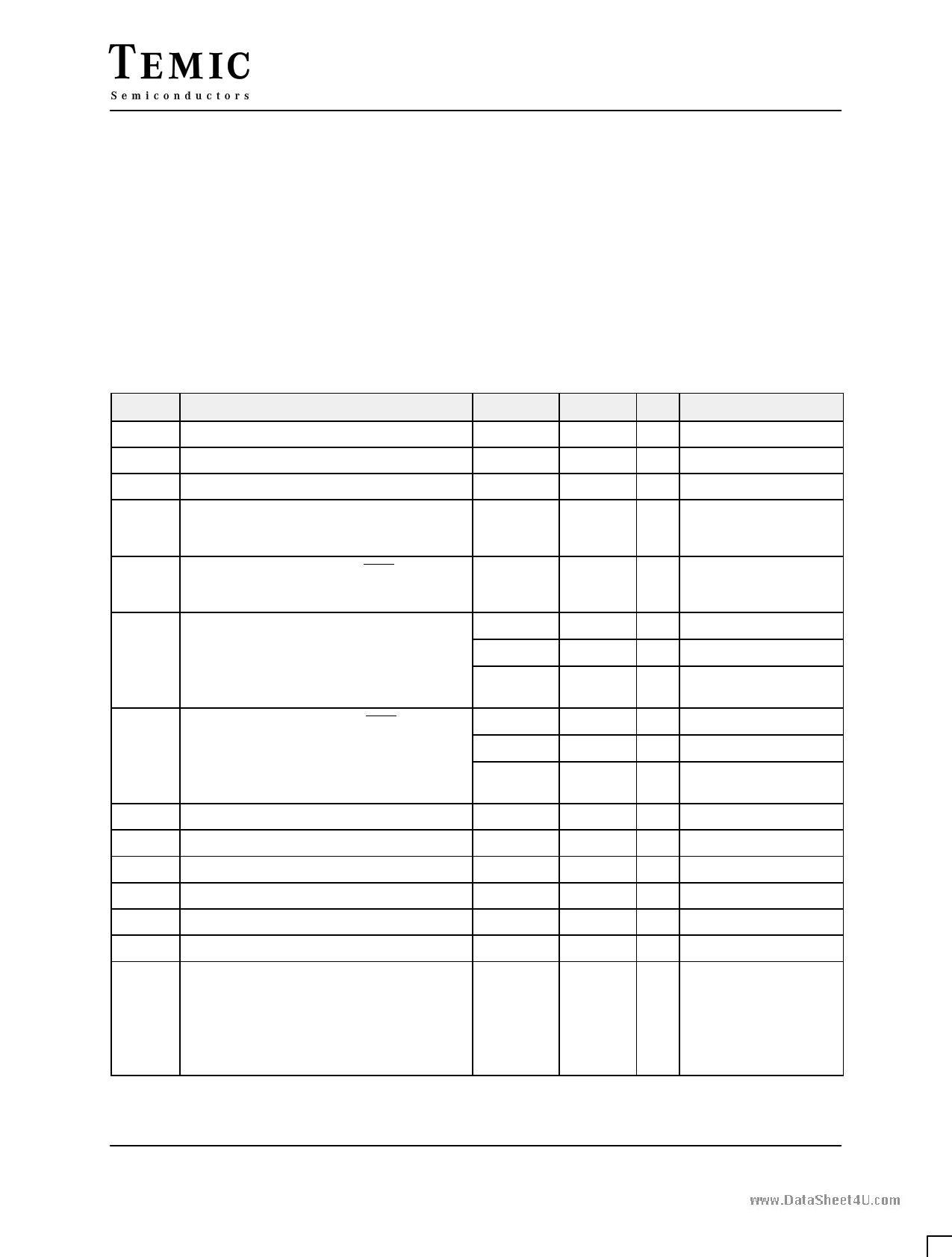
www.DataSheet4U.com
80C32/80C52
Absolute Maximum Ratings*
Ambient Temperature Under Bias :
A = Automotive . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +125°C
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to + 150°C
Voltage on VCC to VSS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.5 V to + 7 V
Voltage on Any Pin to VSS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –0.5 V to VCC + 0.5 V
Power Dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1 W
* This value is based on the maximum allowable die temperature and
the thermal resistance of the package
* Notice
Stresses above those listed under “ Absolute Maximum Ratings” may
cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and
functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above
those indicated in the operational sections of this specification is not
implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for extended
periods may affect device reliability.
DC Parameters
TA = –40°C + 125°C ; VSS = 0 V ; VCC = 5 V ± 10 % ; F = 0 to 36 MHz
SYMBOL
PARAMETER
VIL Input Low Voltage
VIH Input High Voltage (Except XTAL and RST)
VIH1 Input High Voltage (for XTAL and RST)
VOL Output Low Voltage (Port 1, 2 and 3)
VOL1 Output Low Voltage (Port 0, ALE, PSEN)
VOH Output High Voltage Port 1, 2 and 3
VOH1 Output High Voltage (Port 0, ALE, PSEN)
IIL
ILI
ITL
IPD
RRST
CIO
ICC
Logical 0 Input Current (Ports 1, 2 and 3)
Input leakage Current
Logical 1 to 0 Transition Current (Ports 1, 2 and 3)
Power Down Current
RST Pulldown Resistor
Capacitance of I/O Buffer
Power Supply Current
Freq = 1 MHz Icc op
Icc idle
Freq = 6 MHz Icc op
Icc idle
Freq ≥ 12 MHz Icc op = 1.25 Freq (MHz) + 5 mA
Icc idle = 0.36 Freq (MHz) + 2.7 mA
MIN
MAX UNIT TEST CONDITIONS
– 0.5
0.2 Vcc – 0.1 V
0.2 Vcc + 1.4 Vcc + 0.5 V
0.7 Vcc
Vcc + 0.5 V
0.3 V IOL = 100 µA
0.45 V IOL = 1.6 mA (note 2)
1.0 V IOL = 3.5 mA
0.3 V IOL = 200 µA
0.45 V IOL = 3.2 mA (note 2)
1.0 V IOL = 7.0 mA
Vcc – 0.3
V IOH = – 10 µA
Vcc – 0.7
V IOH = – 30 µA
Vcc – 1.5
V IOH = – 60 µA
VCC = 5 V ± 10 %
Vcc – 0.3
V IOH = – 200 µΑ
Vcc – 0.7
V IOH = – 3.2 mA
Vcc – 1.5
V IOH = – 7.0 mA
VCC = 5 V ± 10 %
– 75 µA Vin = 0.45 V
±10 µA 0.45 < Vin < Vcc
– 750
µA Vin = 2.0 V
75 µA Vcc = 2.0 V to 5.5 V (note 1)
50 200 KOhm
10 pF fc = 1 MHz, Ta = 25_C
Vcc = 5.5 V
1.8 mA
1 mA
10 mA
4 mA
MATRA MHS
Rev. G (14 Jan. 97)
11
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 20 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet P-80C32.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| P-80C31 | P80C31 | NXP Semiconductors |
| P-80C32 | P80C32 | ETC |
| P-80C32 | (P-80C32 / P-80C52) CMOS 8-Bit Microcontroller | Temic |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
