
|
|
PDF ATMEGA165P Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | ATMEGA165P | |
| Descripción | 8-bit Microcontroller | |
| Fabricantes | ATMEL Corporation | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de ATMEGA165P (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 30 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
Features
• High Performance, Low Power Atmel® AVR® 8-Bit Microcontroller
• Advanced RISC Architecture
– 130 Powerful Instructions – Most Single Clock Cycle Execution
– 32 × 8 General Purpose Working Registers
– Fully Static Operation
– Up to 16 MIPS Throughput at 16 MHz
– On-Chip 2-cycle Multiplier
• High Endurance Non-volatile Memory segments
– 16 Kbytes of In-System Self-programmable Flash program memory
– 512 Bytes EEPROM
– 1 Kbytes Internal SRAM
– Write/Erase cyles: 10,000 Flash/100,000 EEPROM(1)(3)
– Data retention: 20 years at 85°C/100 years at 25°C(2)(3)
– Optional Boot Code Section with Independent Lock Bits
In-System Programming by On-chip Boot Program
True Read-While-Write Operation
– Programming Lock for Software Security
• JTAG (IEEE std. 1149.1 compliant) Interface
– Boundary-scan Capabilities According to the JTAG Standard
– Extensive On-chip Debug Support
– Programming of Flash, EEPROM, Fuses, and Lock Bits through the JTAG Interface
• Peripheral Features
– Two 8-bit Timer/Counters with Separate Prescaler and Compare Mode
– One 16-bit Timer/Counter with Separate Prescaler, Compare Mode, and Capture Mode
– Real Time Counter with Separate Oscillator
– Four PWM Channels
– 8-channel, 10-bit ADC
– Programmable Serial USART
– Master/Slave SPI Serial Interface
– Universal Serial Interface with Start Condition Detector
– Programmable Watchdog Timer with Separate On-chip Oscillator
– On-chip Analog Comparator
– Interrupt and Wake-up on Pin Change
• Special Microcontroller Features
– Power-on Reset and Programmable Brown-out Detection
– Internal Calibrated Oscillator
– External and Internal Interrupt Sources
– Five Sleep Modes: Idle, ADC Noise Reduction, Power-save, Power-down, and Standby
• I/O and Packages
– 54 Programmable I/O Lines
– 64-lead TQFP and 64-pad QFN/MLF
• Speed Grade:
– ATmega165PV: 0 - 4 MHz @ 1.8V - 5.5V, 0 - 8 MHz @ 2.7V - 5.5V
– ATmega165P: 0 - 8 MHz @ 2.7V - 5.5V, 0 - 16 MHz @ 4.5V - 5.5V
• Temperature range:
– -40°C to 85°C Industrial
• Ultra-Low Power Consumption
– Active Mode:
1 MHz, 1.8V: 330 µA
32 kHz, 1.8V: 10 µA (including Oscillator)
– Power-down Mode:
0.1 µA at 1.8V
– Power-save Mode:
0.6 µA at 1.8V(Including 32 kHz RTC)
Notes: 1. Worst case temperature. Guaranteed after last write cycle.
2. Failure rate less than 1 ppm.
3. Characterized through accelerated tests.
8-bit
Microcontroller
with 16K Bytes
In-System
Programmable
Flash
ATmega165P
ATmega165PV
Preliminary
8019K–AVR–11/10
1 page 
ATmega165P
2.2 Pin Descriptions
2.2.1 VCC
2.2.2 GND
Digital supply voltage.
2.2.3
Ground.
Port A (PA7..PA0)
2.2.4
Port A is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port A output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port A pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port A pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port B (PB7:PB0)
2.2.5
Port B is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port B output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port B pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port B pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port B has better driving capabilities than the other ports.
Port B also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega165P as listed on
“Alternate Functions of Port B” on page 69.
Port C (PC7:PC0)
2.2.6
Port C is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port C output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port C pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port C pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port D (PD7:PD0)
2.2.7
Port D is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port D output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port D pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
resistors are activated. The Port D pins are tri-stated when a reset condition becomes active,
even if the clock is not running.
Port D also serves the functions of various special features of the ATmega165P as listed on
“Alternate Functions of Port D” on page 72.
Port E (PE7:PE0)
Port E is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull-up resistors (selected for each bit). The
Port E output buffers have symmetrical drive characteristics with both high sink and source
capability. As inputs, Port E pins that are externally pulled low will source current if the pull-up
8019K–AVR–11/10
5
5 Page 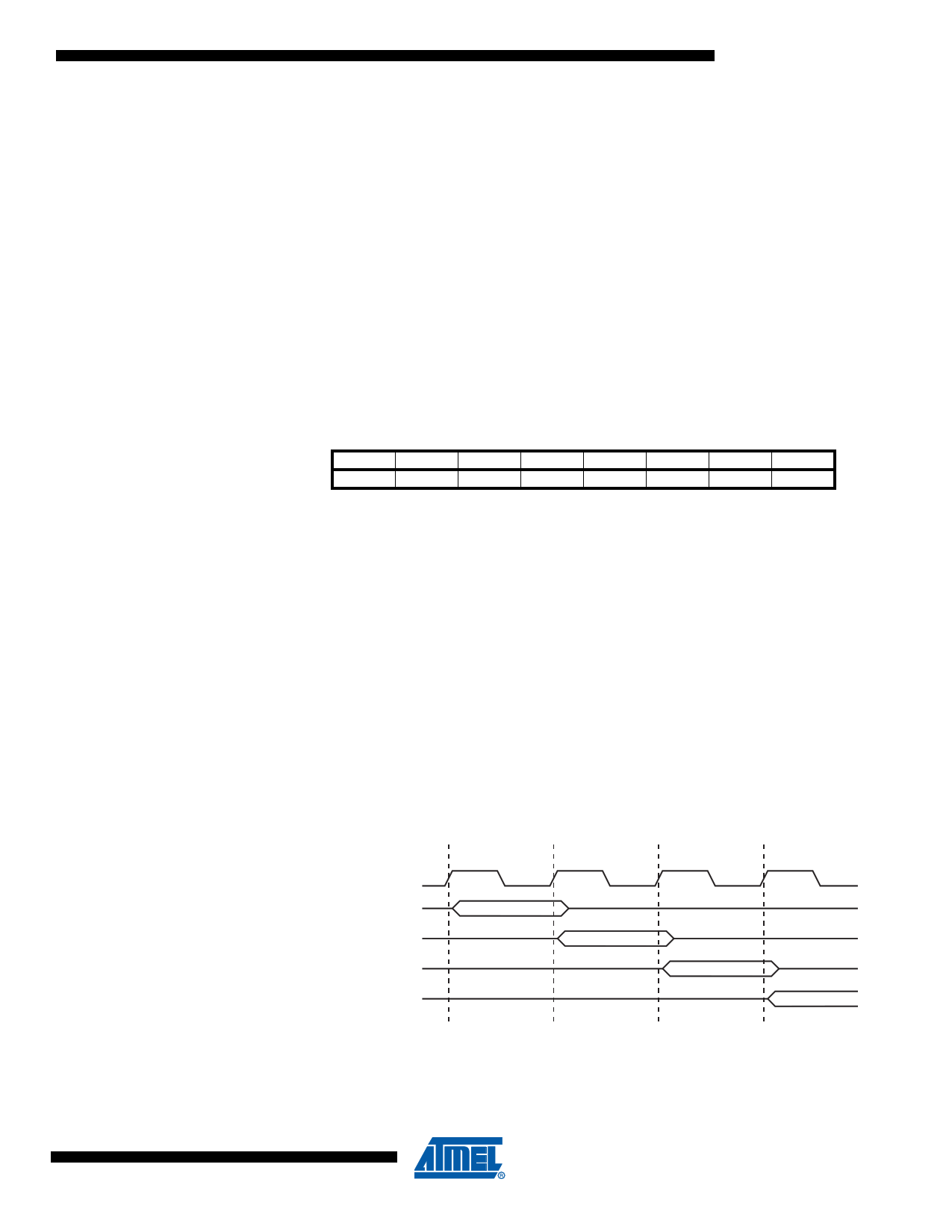
ATmega165P
5.3.1
The Stack Pointer points to the data SRAM Stack area where the Subroutine and Interrupt
Stacks are located. This Stack space in the data SRAM must be defined by the program before
any subroutine calls are executed or interrupts are enabled. The Stack Pointer must be set to
point above 0xFF. The Stack Pointer is decremented by one when data is pushed onto the Stack
with the PUSH instruction, and it is decremented by two when the return address is pushed onto
the Stack with subroutine call or interrupt. The Stack Pointer is incremented by one when data is
popped from the Stack with the POP instruction, and it is incremented by two when data is
popped from the Stack with return from subroutine RET or return from interrupt RETI.
The AVR Stack Pointer is implemented as two 8-bit registers in the I/O space. The number of
bits actually used is implementation dependent. Note that the data space in some implementa-
tions of the AVR architecture is so small that only SPL is needed. In this case, the SPH Register
will not be present.
SPH and SPL – Stack Pointer High and Low
Bit
0x3E (0x5E)
0x3D (0x5D)
Read/Write
Initial Value
15 14 13 12 11 10
9
8
–
–
–
–
–
SP10
SP9
SP8
SPH
SP7 SP6 SP5 SP4 SP3 SP2 SP1 SP0 SPL
76543210
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
R/W
00000000
00000000
5.4 Instruction Execution Timing
This section describes the general access timing concepts for instruction execution. The AVR
CPU is driven by the CPU clock clkCPU, directly generated from the selected clock source for the
chip. No internal clock division is used.
Figure 5-2 shows the parallel instruction fetches and instruction executions enabled by the Har-
vard architecture and the fast-access Register File concept. This is the basic pipelining concept
to obtain up to 1 MIPS per MHz with the corresponding unique results for functions per cost,
functions per clocks, and functions per power-unit.
Figure 5-2. The Parallel Instruction Fetches and Instruction Executions
T1 T2 T3
T4
clkCPU
1st Instruction Fetch
1st Instruction Execute
2nd Instruction Fetch
2nd Instruction Execute
3rd Instruction Fetch
3rd Instruction Execute
4th Instruction Fetch
Figure 5-3 on page 12 shows the internal timing concept for the Register File. In a single clock
cycle an ALU operation using two register operands is executed, and the result is stored back to
the destination register.
8019K–AVR–11/10
11
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 30 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet ATMEGA165P.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| ATmega165 | 8-bit Microcontroller | ATMEL Corporation |
| ATmega165A | 8-bit Atmel Microcontroller | ATMEL Corporation |
| ATMEGA165P | 8-bit Microcontroller | ATMEL Corporation |
| ATmega165PA | 8-bit Atmel Microcontroller | ATMEL Corporation |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
