
|
|
PDF PFS725EG Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | PFS725EG | |
| Descripción | (PFS704 - PFS729) High Power PFC Controller | |
| Fabricantes | Power Integrations | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de PFS725EG (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 30 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
PFS704-729EG
HiperPFS™ Family
High Power PFC Controller with Integrated
High-Voltage MOSFET
Key Benefits
• Single chip solution for boost power factor correction (PFC)
• EN61000-3-2 Class C and D compliant
• High light load efficiency at 10% and 20% load
• >95% efficiency from 10% load to full load
• <130 mW no-load consumption at 230 VAC with output in
regulation
• <50 mW no-load consumption at 230 VAC in remote off state
• Frequency adjusted over line voltage, and line cycle
• Spread-spectrum across >60 kHz window to simplify EMI
filtering requirements
• Lower boost inductance
• Provides up to 1 kW peak output power
• >1 kW peak power delivery in power limit voltage regulation
mode
• High integration allows smaller form factor, higher power density
designs
• Incorporates control, gate driver, and high-voltage power
MOSFET
• Internal current sense reduces component count and system
losses
• Protection features include: UV, OV, OTP, brown-in/out, cycle-
by-cycle current limit, and power limiting for overload protection
• Halogen free and RoHS compliant
Applications
• PC
• Printer
• LCD TV
• Video game consoles
• High power adaptors
• High power LED lighting
• Industrial and appliance
• Generic PFC converters
Output Power Table
Product
Maximum Continuous
Output Power Rating at
90 VAC
Peak Output Power
Rating at 90 VAC
PFS704EG
110 W
120 W
PFS706EG
PFS708EG
PFS710EG
PFS712EG
PFS714EG
PFS716EG
140 W
190 W
240 W
300 W
350 W
388 W
150 W
205 W
260 W
320 W
385 W
425 W
Product
Maximum Continuous
Output Power Rating at
180 VAC
Peak Output Power
Rating at 180 VAC
PFS723EG
PFS724EG
PFS725EG
PFS726EG
PFS727EG
PFS728EG
PFS729EG
255 W
315 W
435 W
540 W
675 W
810 W
900 W
280 W
350 W
480 W
600 W
750 W
900 W
1000 W
Table 1. Output Power Table (see Notes on page 9)
+
VCC
DV
VCC
AC
IN
HiperPFS
CONTROL
FB
SG
DC
OUT
www.powerint.com
Figure 1. Typical Application Schematic.
PI-6021-110810
December 2011
Free Datasheet http://www.datasheet4u.com/
1 page 
PFS704-729EG
Functional Description
The HiperPFS is a variable switching frequency boost PFC
solution. More specifically, it employs a constant amp-second
on-time and constant volt-second off-time control algorithm.
This algorithm is used to regulate the output voltage and shape
the input current to comply with regulatory harmonic current
limits (high power factor). Integrating the switch current and
controlling it to have a constant amp-sec product over the
on-time of the switch allows the average input current to follow
the input voltage. Integrating the difference between the output
and input voltage maintains a constant volt-second balance
dictated by the electro-magnetic properties of the boost inductor
and thus regulates the output voltage and power.
VE
Latch
RESET
Latch
SET
Gate
Drive (Q)
Maximum
ON-time
Minimum
OFF-time
VOFF
IS dt
(VOUT-VIN)dt
Timing
Supervisor
More specifically, the control technique sets constant volt-
seconds
that:
for
the
off-time
(tOFF).
The off-time is controlled such
(1)
Since the volt-seconds during the on-time must equal the
volt-seconds during the off-time, to maintain flux equilibrium in
t he PFC c hoke, the on-time (tON) is co ntrolled s uch that:
(2)
The controller also sets a constant value of charge during each
on-cycle of the power MOSFET. The charge per cycle is varied
gradually over many switching cycles in response to load
changes so it can be regarded as substantially constant for a
half line cycle. With this constant charge (or amp-second)
control, the following relationship is therefore also true:
(3)
S ubstitutin g tON from (2) into (3) gives:
(4)
The relationship of (4) demonstrates that by controlling a constant
amp-second on-time and constant volt-second off-time, the input
cpurorrveidnitnIgIN tihsepfruonpdoarmtioennatlatlorethqeuirinepmuetnvtooltfapgoewVeINr,ftahcetorerfocorerrection.
Figure 4. Idealized Converter Waveforms.
cycle on-time. Internally the difference between the input and
output voltage is derived and the resultant is scaled, integrated,
and compared to a voltage reference (VOFF) to determine the
cycle off-time. Careful selection of the internal scaling factors
produce input current waveforms with very low distortion and
high power factor.
The input voltage is internally synthesized using the switch duty
cycle and a 7 kHz low pass filter. This synthesized input voltage
representation is subtracted from a fixed reference voltage (6 V)
to derive
Figure 3.
a
current
source
proportional
to
(VO-VIN).
Please refer to
TLhineeVFOeLeTdA-GFEorMwOarNdITSOcRal(iVng) pFinacctuorrre(nMt OisN)used internally to
derive the peak of the input line voltage which is used to scale
tThheisgcaoinntorfibtuhteiocnuirsrernetqsueirnesdetosigrendaul ctherothueghdythneamMicONravanrgiaebolef .the
control feedback signal as well maintain a constant loop gain
over the operating input line range. This line-sense feed-
forward gain adjustment is proportional to the square of the
peak rectified AC line voltage and is adjusted as a function of V
pin current. The line-sense feed-forward gain is also important
in providing a switch power limit over the input line range.
Besides modifying brown- in/out thresholds, the V pin resistor
also affects power limit of the device
This control produces a continuous mode power switch current
waveform that varies both in frequency and peak current value
across a line half-cycle to produce an input current proportional
to the input voltage.
Control Engine
The controller features a low bandwidth error-amplifier which
connects its non-inverting terminal to an internal voltage
reference of 6 V. The inverting terminal of the error-amplifier is
available on the external FEEDBACK pin which connects to the
external feedback resistor divider, transient load speed-up and
compensation networks to regulate the output voltage.
The internal sense-FET switch current is integrated and scaled
cboymthpeairnepduwt vitohlttahgeeeprreoar-kadmeptelicfietorrscigunrrael n(Vt Es)etnosdeegtearinm(iMneONth) eand
www.powerint.com
This characteristic is optimized to maintain a relatively constant
internal error-voltage level at full load from an input line of 100
to 230 VAC input (PFS704-716).
Beyond the specified peak power rating of the device, the
internal power limit feature will regulate the output voltage
below the set regulation threshold as a function of output
overload beyond the peak power rating. Figure 5 illustrates the
typical regulation characteristic as function of load.
Soft-Start with Pin-to-Pin Short-Circuit Protection
Since the FEEDBACK pin is the interface for output voltage
regulation (resistor voltage divider to output voltage) as well as
loop compensation (series RC), the typical application circuit of
the HiperPFS requires an external transistor network to overcome
the inherently slow feedback loop response. Specifically, an
5
Rev. D 12/11
Free Datasheet http://www.datasheet4u.com/
5 Page 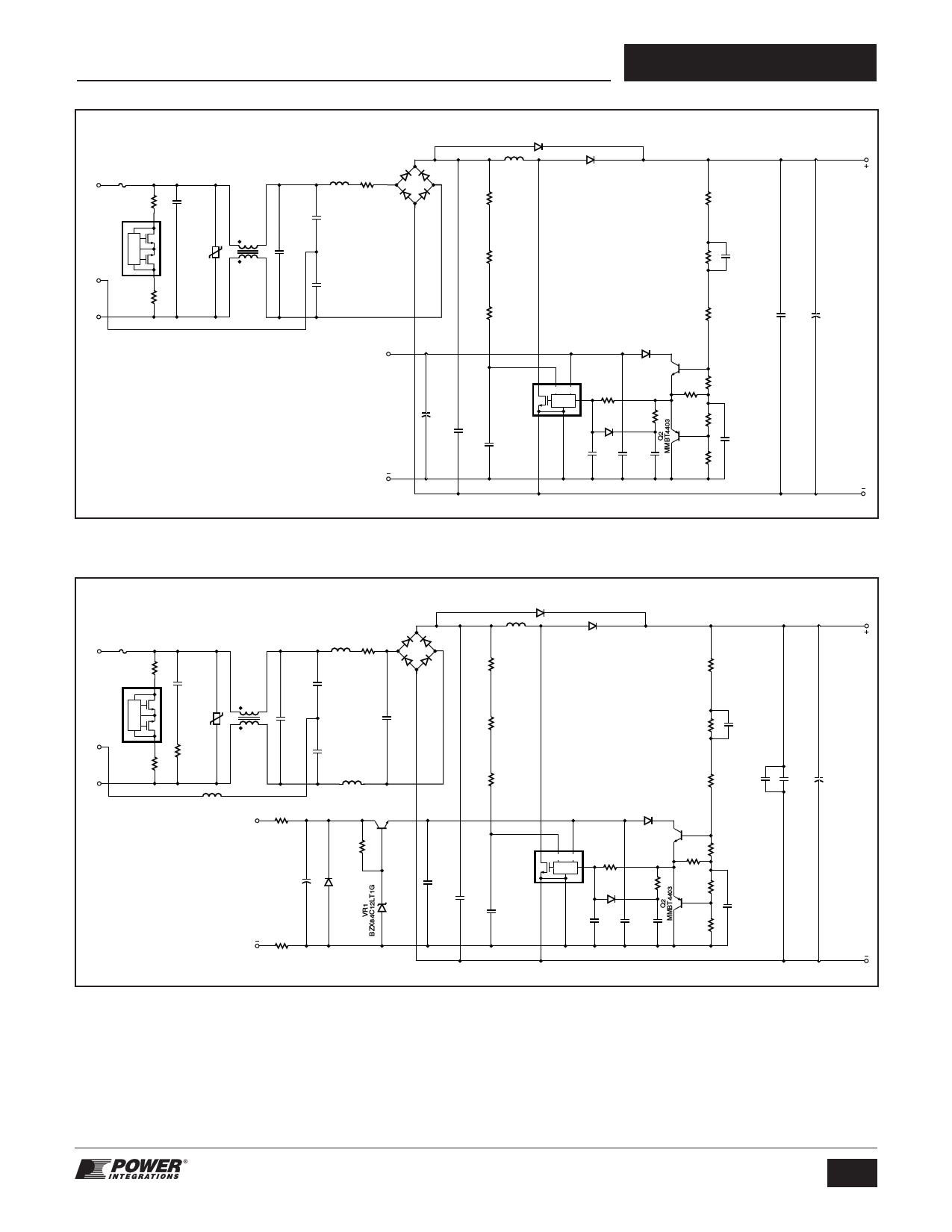
PFS704-729EG
F1
3.15 A
L
R1
750 kΩ
D1
C3
220 nF
275 VAC
CAPZero
U2
CAP002DG
RV1
320 VAC
E D2
R2
750 kΩ
N
L1
10 mH
L2
100 µH
BR1
RT1
10 Ω
3KBP06M
600 V
tO
C19
220 nF
275 VAC
C4
100 pF
250 VAC
C5
100 pF
250 VAC
+
12 V
Auxiliary
Power
Supply
D1
1N5408
L5
1.7 mH
R4
1.5 MΩ
1%
D2
STTH3R06U
R9
1.5 MΩ
1%
R19
1.5 MΩ
1%
R11
732 kΩ
1%
C16
100 nF
200 V
C20
47 µF
25 V
R5
1 MΩ
1%
D4
1N4148
R10
1.6 MΩ
1%
C14
10 nF
1 kV
C7
470 nF
400 V
D
HiperPFS
U1
PFS708EG
S
C12
100 nF
50 V
V VCC
CONTROL
FB
R7
2 kΩ
Q1
MMBT4401
R15
160 kΩ
D3 R8
G
BAV116 3.01 kΩ
130 V
1%
R13
2.21 kΩ
1%
C11
10 nF
50 V
C18
1 µF
25 V
C13
4.7 µF
25 V
R14
57.6 kΩ
1%
R12
2.21 kΩ
1%
C17
470 pF
100 V
Figure 12. 180 W PFC using PFS708EG.
+
C15
150 µF
450 V
DC
OUT
PI-6229-110210
F1
8A
L
R1
220 kΩ
D1
CAPZero
U2
CAP006DG
E D2
R2
220 kΩ
N
C3
680 nF
275 VAC
RV1
320 VAC
R18
10 Ω
2W
L1
14 mH
L2
100 µH
BR1
RT1
10 Ω
GBU10J
600 V
tO
C19
1 µF
275 VAC
C4
680 pF
250 VAC
C6
100 nF
275 VAC
C5
680 pF
250 VAC
L4
Ferrite Bead
R6
100 Ω
+
15 V
Auxiliary
Power
Supply
C8
47 µF
50 V
L3
100 µH
Q3
MMBT4401LT1G
R17
3.01 kΩ
1%
D5
DL4001
R16
100 Ω
D1
1N5408
L5
2.04 mH
R4
3 MΩ
1%
D2
STTH12R06
R9
1.5 MΩ
1%
R19
3 MΩ
1%
R11
732 kΩ
1%
C16
100 nF
200 V
C20
100 nF
25 V
R5
3 MΩ
1%
R10
1.6 MΩ
1%
C21
10 nF
1 kV
D4
1N4148
C7
1.5 µF
400 V
D
HiperPFS
U1
PFS729EG
S
C12
47 nF
50 V
V VCC
CONTROL
FB
R7
2 kΩ
Q1
MMBT4401
R15
160 kΩ
D3 R8
G
BAV116 3.01 kΩ
130 V
1%
R13
2.21 kΩ
1%
C11
10 nF
50 V
C18
1 µF
25 V
C13
4.7 µF
25 V
R14
57.6 kΩ
1%
R12
2.21 kΩ
1%
C17
470 pF
100 V
Figure 13. 900 W PFC using PFS729EG.
+
C14
10 nF
1 kV
C15
820 µF
450 V
DC
OUT
PI-6230-111110
www.powerint.com
11
Rev. D 12/11
Free Datasheet http://www.datasheet4u.com/
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 30 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet PFS725EG.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| PFS725EG | (PFS704 - PFS729) High Power PFC Controller | Power Integrations |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
